Late-time tails in nonlinear evolutions of merging black holes
Marina De Amicis, Hannes Rüter, Gregorio Carullo, Simone Albanesi, C. Melize Ferrus, Keefe Mitman, Leo C. Stein, Vitor Cardoso, Sebastiano Bernuzzi, Michael Boyle, Nils Deppe, Lawrence E. Kidder, Jordan Moxon, Alessandro Nagar, Kyle C. Nelli, Harald P. Pfeiffer, Mark A. Scheel, William Throwe, Nils L. Vu, Anıl Zenginoğlu
Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 171401 (2025) [arXiv:2412.06887] [doi:10.1103/2brx-xnyr]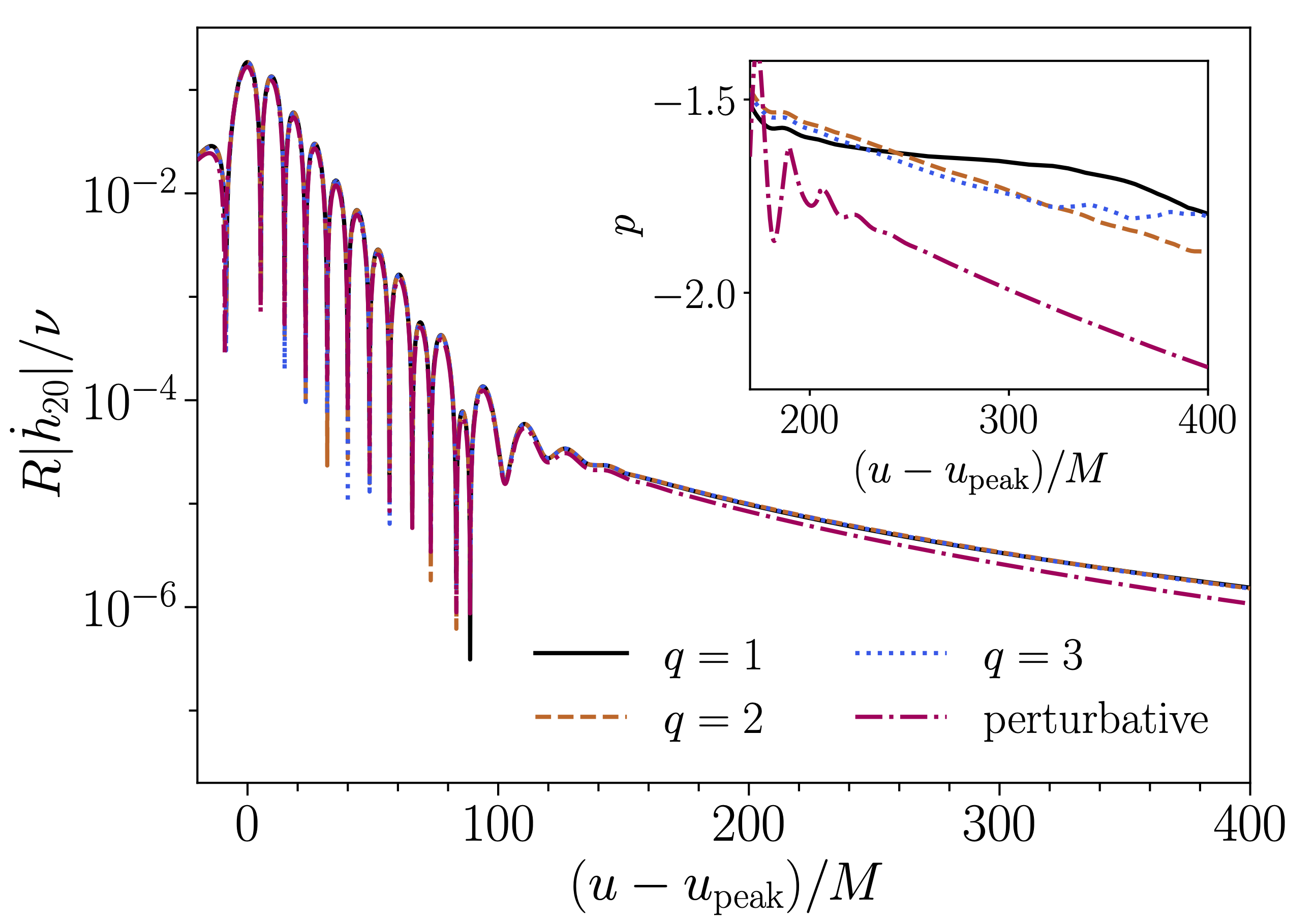
We uncover late-time gravitational-wave tails in fully nonlinear 3+1 dimensional numerical relativity simulations of merging black holes, using the highly accurate SpEC code. We achieve this result by exploiting the strong magnification of late-time tails due to binary eccentricity, recently observed in perturbative evolutions, and showcase here the tail presence in head-on configurations for several mass ratios close to unity. We validate the result through a large battery of numerical tests and detailed comparison with perturbative evolutions, which display striking agreement with full nonlinear ones. Our results offer yet another confirmation of the highly predictive power of black hole perturbation theory in the presence of a source, even when applied to nonlinear solutions. The late-time tail signal is much more prominent than anticipated until recently, and possibly within reach of gravitational-wave detectors measurements, unlocking observational investigations of an additional set of general relativistic predictions on the long-range gravitational dynamics.
